Is Bile Duct Cancer Lurking Within? Understand Its Signs and Treatments
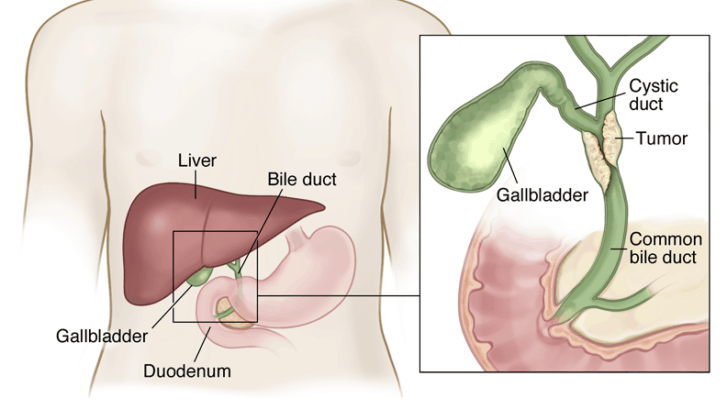
Dealing with the complexities of bile duct cancer can be challenging. Bile duct cancer, medically termed cholangiocarcinoma, affects the thin tubes carrying bile from the liver to the intestine. Globally, this cancer accounts for a small portion of overall cancer diagnoses, representing around 3% of gastrointestinal cancers. Despite its rarity, its impact can be profound due to its challenging nature.
The cornerstone of treating bile duct cancer often involves surgery, aiming to remove the cancerous growth. However, understanding the intricacies of bile duct cancer surgery becomes crucial for patients and their families, as it significantly influences treatment outcomes and recovery.
This blog aims to explain and explore the signs and treatments of surgery for bile duct cancer.
What is a Bile Duct?
The bile duct is a thin tube that runs from the liver to the small intestine. It’s about 4 to 5 inches long. The bile duct’s primary purpose is to move a fluid called bile. It transports bile from the liver to the gallbladder, then to the small intestine. Bile helps digest the fats in foods.
What is Bile Duct Cancer?
Bile duct cancer, or cholangiocarcinoma, develops in the tubes (bile ducts) that carry bile from the liver to the small intestine. It is a rare but severe cancer that impacts the bile ducts, hindering the flow of bile and digestion and leading to various health complications.
Dr. Deep Goel has extensive experience treating bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma). With over 500 successful treatments and a commendable success rate, his advanced methods and surgeries have made a big difference for patients who have bile duct cancer.
What are the Types of Bile Duct Cancer?
Bile duct cancers are named for where they develop. Common types include:
- Intrahepatic bile duct cancers: These cancers develop in the smaller bile duct branches located inside the liver.
- Extrahepatic bile duct cancers: These cancers develop in the branches of the bile duct outside the liver. There are two main types:
- Perihilar bile duct cancers: These are the most common types of bile duct cancer. They develop at the hilum, where two smaller branches leave the liver and merge into one duct.
- Distal extrahepatic bile duct cancers: These are found further down the bile duct, near the small intestine.
More than 95% of bile duct cancers are adenocarcinomas. Bile duct adenocarcinomas develop from the mucus glands that line the inside of the duct.
What are the Risk Factors for Bile Duct Cancer?
Ongoing research helps better understand bile duct cancer and its risk factors. This helps with early detection and prevention. Some common risk factors for bile duct cancer include:
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Chronic ulcerative colitis
- Choledochal cysts
- Cirrhosis
- Infection with Hepatitis B or C
- Infection with a Chinese liver fluke parasite
- Old age
- Obesity
- Type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- Exposure to chemicals, such as dioxins or nitrosamines
“Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial. Avoid smoking, manage chronic conditions like diabetes, and stay cautious of liver infections. Regular check-ups and a balanced diet can significantly reduce the risk of bile duct cancer. Remember, small lifestyle changes make a big difference in preventing this disease,” says Dr. Deep.
What are the Signs & Symptoms of Bile Duct Cancer?
There are several symptoms of bile duct cancer. However, these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions. Be sure to speak with your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes)
- Pain in the abdomen
- Fever
- Itchy skin
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
How is Bile Duct Cancer Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosing bile duct cancer involves several steps. Your healthcare provider will conduct a physical examination and assess your medical history. Blood tests may reveal abnormalities related to liver function. Imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasounds help visualize the liver and bile ducts for potential tumors or blockages. A tissue sample (biopsy) might be taken for analysis to confirm cancer.
Treatment for bile duct cancer varies based on the cancer’s stage, location, and overall health. Possible options include:
- Surgery: Removing the tumor or affected portion of the bile duct
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells
- Chemotherapy: Administering drugs to kill cancer cells
- Targeted Therapy: Medications targeting specific abnormalities in cancer cells
Clinical trials might offer novel treatments. Collaborating closely with your healthcare team helps tailor the best treatment plan for you, considering your preferences and overall health.
A happy patient of Dr. Deep mentioned that “ Choosing Dr. Deep Goel was a turning point in treating my bile duct cancer. I received exceptional care and expertise. The medical team was dedicated and precise in diagnosing and treating my problem. The high-tech facilities and caring staff made me feel safe and supported.”
What is the Cost of Bile Duct Cancer Surgery in India?
In India, Bile Duct Cancer Treatment costs for Indian patients range from Rs.2,00,000 to Rs.2,70,000. For international patients, it’s approximately USD 4,050 to USD 4,950. This treatment typically involves a 4-day hospital stay and 40 days outside the hospital.
However, the cost may vary based on the patient’s diagnosis and chosen facilities. The overall expenses are influenced by treatment procedures, medical facilities, and post-hospital care, determining the final cost for patients. These factors collectively impact the patient’s treatment expenses.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing bile duct cancer, although rare, is crucial due to its significant impact. Early recognition of its signs and symptoms is pivotal in timely diagnosis and treatment. With surgery as a cornerstone, coupled with radiation, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies, tailored treatment plans offer hope for improved outcomes. However, treatment costs vary based on multiple factors, necessitating a personalized approach and comprehensive healthcare support for patients navigating this challenging journey.
FAQs
Is bile duct cancer hereditary?
There’s no clear evidence suggesting a solid hereditary link to bile duct cancer.
Can lifestyle changes reduce the risk of bile duct cancer?
While not definitive, maintaining a healthy lifestyle may lower the risk.
Are all bile duct tumors cancerous?
Not all tumors in the bile ducts are cancerous; some could be benign or non-cancerous.
Is bile duct cancer treatable if diagnosed in later stages?
Treatment options vary, but early detection generally offers better treatment outcomes.
What follow-up care is required after bile duct cancer treatment?
Regular monitoring and follow-ups are essential to monitor for recurrence or new developments.

